Sprain vs Strain What's the Difference?
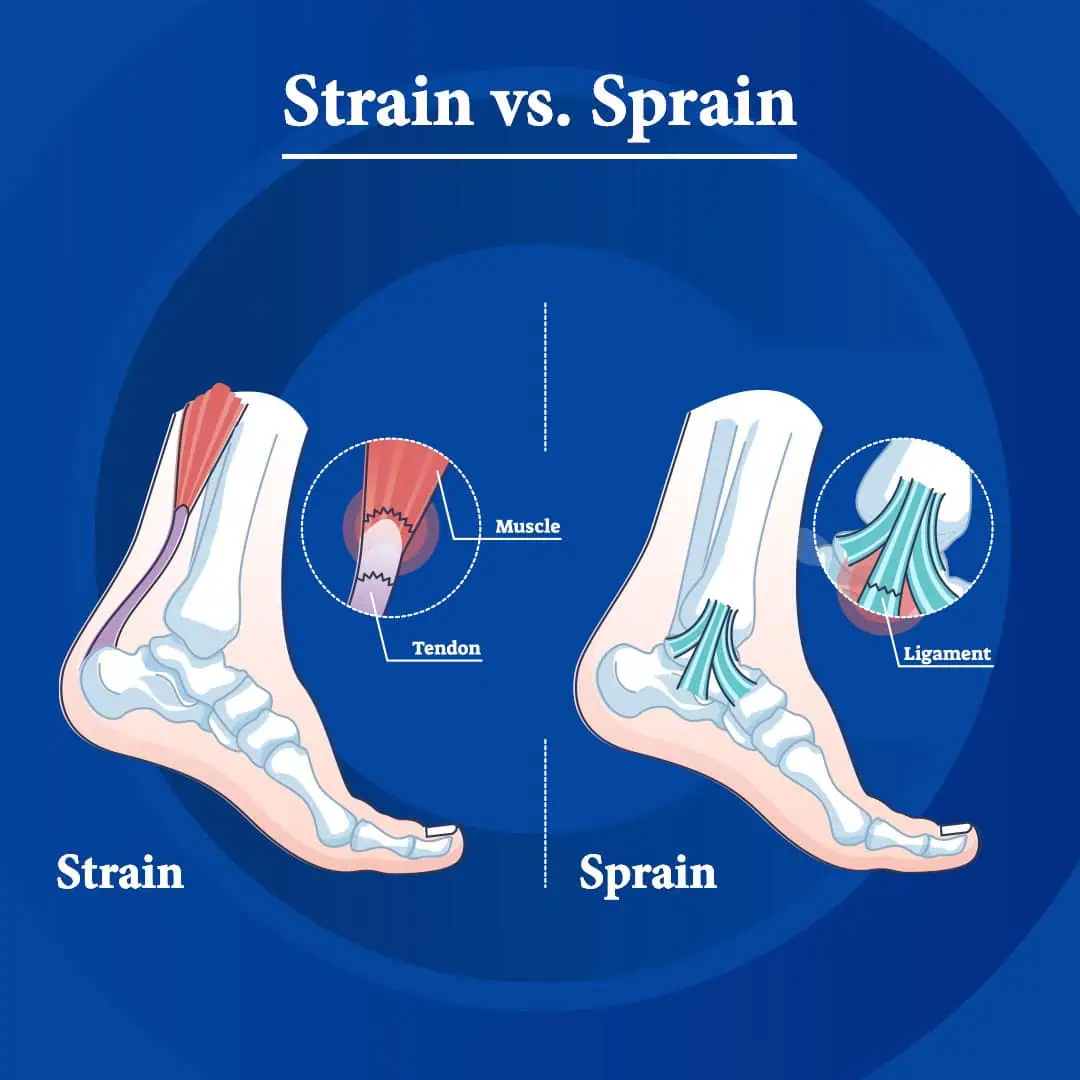
Sprains and strains are common injuries that affect the body's soft tissues, but they involve different structures and require distinct approaches to treatment. A sprain refers to an injury to a ligament, the tissue connecting bones, while a strain involves damage to a muscle or tendon, which connects muscles to bones. Understanding the differences between these injuries, their signs and symptoms, and associated conditions like edema is crucial for effective treatment and recovery
At The Right Spinal Clinic, a trusted provider of chiropractic care and physical therapy in Tampa, FL, we specialize in diagnosing and treating these injuries to help our patients recover quickly and safely.
Key Takeaways:
- Sprains and Strains Differ: Sprains involve ligament injuries (e.g., ankle, wrist), while strains affect muscles or tendons (e.g., lower back, hamstrings). Understanding these differences is crucial for proper treatment.
- Recognize Symptoms: Sprains typically cause joint pain, swelling, and bruising, while strains result in muscle pain, spasms, and weakness. Identifying the location and type of pain can help differentiate between the two.
- Initial Treatment with RICE: Both injuries benefit from the RICE method—Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation—along with over-the-counter pain relief to manage symptoms in the early stages.
- Seek Professional Care for Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe pain, significant swelling, visible deformities, or difficulty bearing weight, consult a healthcare or sports medicine provider for further evaluation and possible imaging tests like MRI.
What is a Sprain?
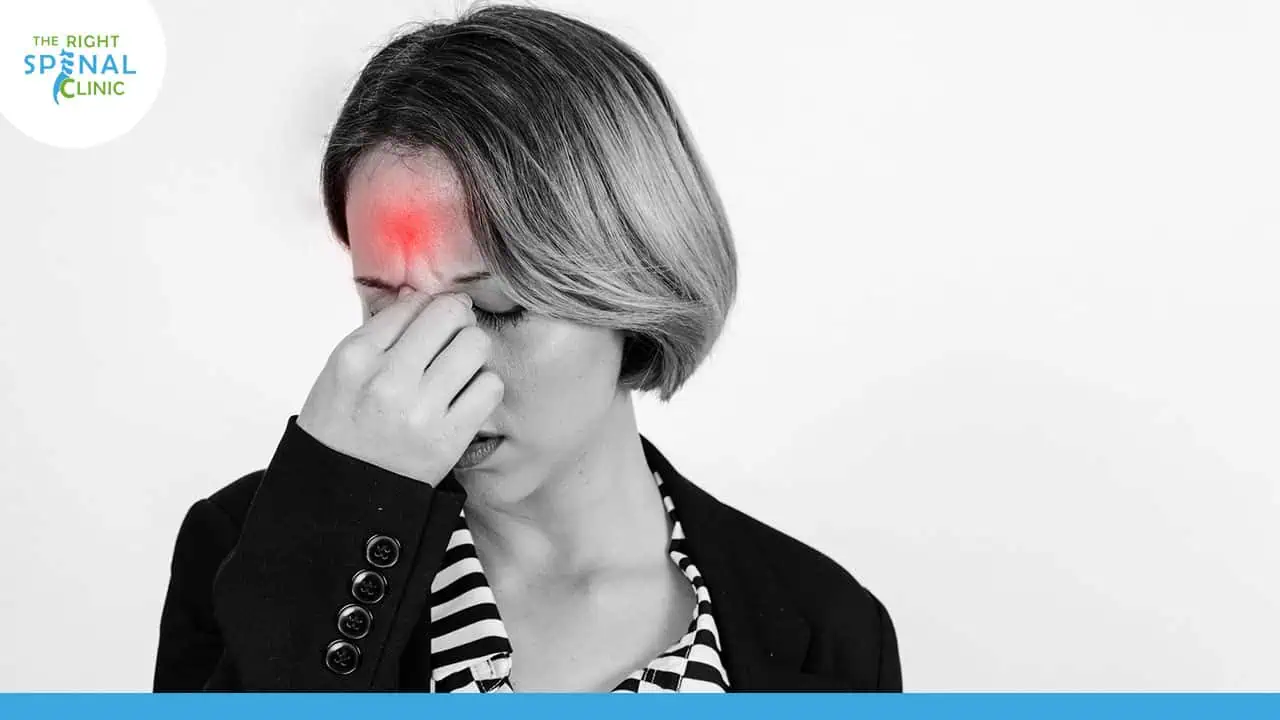
A sprain occurs when ligaments, which connect bones at joints, are stretched or torn. Sprains often affect the ankle, wrist, or thumb due to sudden twists or falls, leading to pain, swelling, bruising, and limited range of motion. Severe cases can cause joint instability.
Signs and Symptoms of a Sprain
According to the Mayo Clinic, common symptoms of a sprain include:
- Pain: Discomfort in the joint, worsening with movement.
- Swelling: Puffiness around the injury.
- Bruising: Skin discoloration around the joint.
- Limited Range of Motion: Stiffness or instability.
- Popping Sensation: A possible tear at the moment of injury.
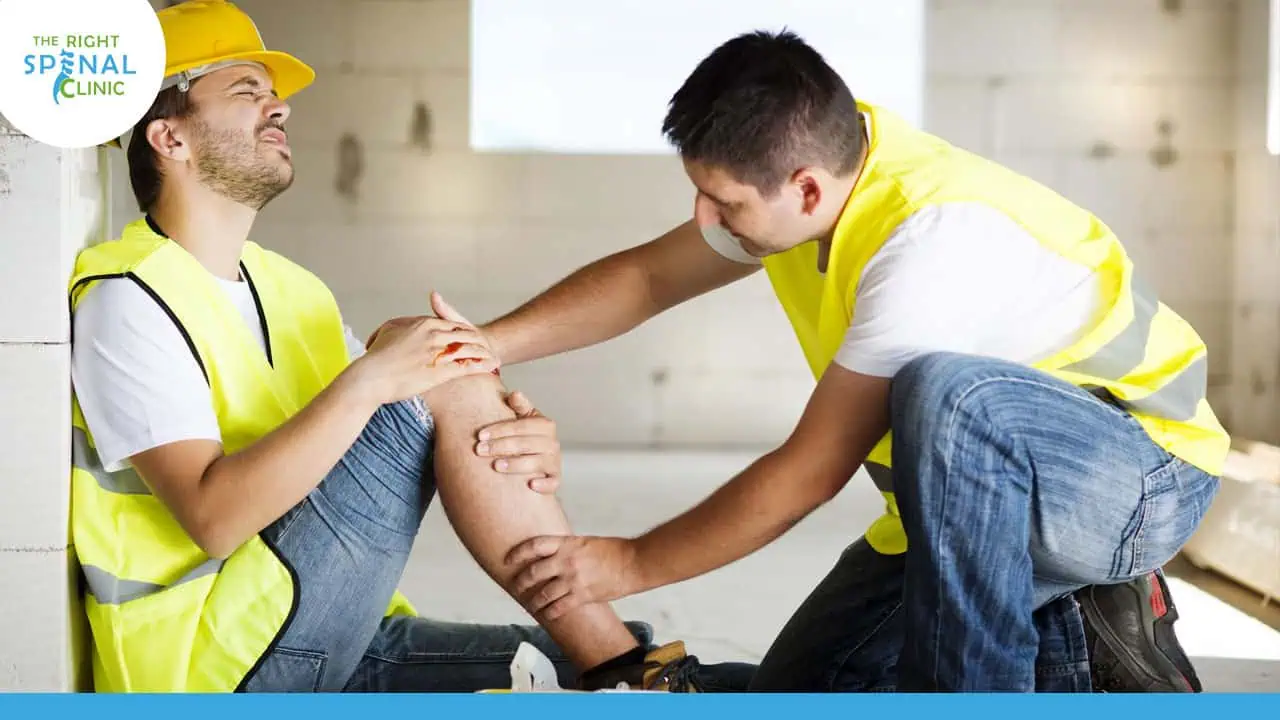
Common Causes of Sprains
Sprains often occur during activities that place stress on the joints, particularly when the body is subjected to sudden movements or impacts. Common causes include:
- Sports Injuries: Activities like basketball, tennis, or running.
- Accidents and Falls: Twisting or bending joints unnaturally.
- Improper Footwear: Lack of support increases the risk.
- Overextension: Exceeding the normal range of motion.
These activities often place undue stress on the ligaments, making sprains a common occurrence in both everyday life and athletic pursuits.
What is a Strain?
According to the Cleveland Clinic, Strains involve overstretching or tearing of muscles or tendons, commonly affecting the lower back, hamstrings, and shoulders. Strains vary from mild to severe, with symptoms like sharp pain, muscle spasms, and weakness.
Signs and Symptoms of a Strain
The symptoms of a strain can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but common signs include:
- Pain: Sharp or aching in the affected area.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions.
- Swelling: Inflammation at the site.
- Limited Movement: Reduced flexibility and strength.
- Bruising: Discoloration of the skin.
- Weakness: Difficulty performing activities.
Common Causes of Strains
Strains often result from activities or actions that place excessive stress on muscles or tendons, leading to overstretching or tearing. Common causes include:
- Overexertion: Intense physical activity.
- Sudden Movements: Abrupt motions like sprinting.
- Improper Technique: Incorrect form in exercises.
- Repetitive Motion: Continuous physical activity.
- Lack of Warming Up: Tight muscles due to inadequate warm-up.
These factors contribute to the likelihood of experiencing a strain, particularly during physical activities or situations that demand sudden or repetitive muscle use.
Comparing Sprains and Strains
While sprains and strains are both soft tissue injuries, they affect different parts of the body and present with distinct symptoms. Understanding these differences is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Pain: Both sprains and strains cause pain, but the location differs. Sprain pain typically occurs around the joint where the ligament is injured, while strain pain is localized in the muscle or tendon.
- Swelling: Swelling is common in both injuries, but in sprains, it often appears around the joint, accompanied by bruising. In strains, the swelling occurs directly over the affected muscle or tendon.
- Bruising: Sprains are more likely to result in noticeable bruising around the joint, especially if the ligament is torn. Strains may also cause bruising, but it is usually less pronounced and located over the muscle.
- Range of Motion: Sprains often lead to joint instability and reduced range of motion due to ligament damage. Strains, on the other hand, primarily limit the movement and flexibility of the affected muscle.
- Muscle Spasms: Strains can cause muscle spasms, where the muscle involuntarily contracts, causing pain and stiffness. This symptom is less common in sprains.
Diagnosis and Initial Steps
Differentiating between a sprain and a strain can be challenging because both injuries share common symptoms like pain and swelling. However, identifying the type of injury early can guide your initial response:
- Location of Pain: Pain centered around a joint, particularly with instability or difficulty moving, suggests a sprain. Pain localized within a muscle, especially after overexertion, points to a strain.
- Signs and Symptoms: Mild cases often improve with rest, ice packs, compression using an elastic bandage, and elevation (RICE). Monitoring these symptoms closely will help you assess if further care is needed.
- Initial Home Care: Apply RICE and consider over-the-counter medication like ibuprofen or paracetamol for pain management. Pay attention to any signs of improvement or worsening symptoms over the next few days.
When to Seek Professional Care
While many sprains and strains can initially be managed at home, there are clear indicators that professional evaluation is necessary:
- Severe Symptoms: Persistent or severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest or RICE, significant swelling, or an inability to bear weight may indicate a serious injury such as a complete tear.
- Visible Deformity: Noticeable lumps, bumps, or misalignment around the joint or muscle require immediate medical attention.
- Numbness or Tingling: These sensations could indicate nerve involvement, necessitating prompt medical evaluation.
- Difficulty Bearing Weight: Inability to bear weight on the affected limb or significant difficulty in using the injured area means you should consult a healthcare provider.
If any of these symptoms are present, consult a healthcare professional, such as a physician or physical therapist, for a detailed physical examination, review of your medical history, and potentially imaging tests like MRI or CT scan. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment are crucial for preventing complications and promoting effective recovery.
Treatment Options for Sprains and Strains
When dealing with sprains and strains, prompt and appropriate treatment is crucial for effective recovery. Both types of injuries require careful management to reduce pain, swelling, and promote healing. While some treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the injury, several general strategies can help manage symptoms and support recovery.
Immediate Self-Care Strategies
RICE Method: The RICE method is a widely recommended approach for managing both sprains and strains in the initial stages of injury. It involves:
- Rest: Avoid using the injured area to prevent further damage and allow the tissues to heal.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the injured area for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours to reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage to apply gentle pressure around the injured area, which helps control swelling. Ensure it’s not too tight to avoid restricting blood flow.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area elevated above the level of the heart to help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage pain and inflammation associated with sprains and strains. Always follow the dosage instructions on the label and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
Immobilization: For more severe cases, immobilizing the injured area with a splint or brace can provide support and prevent further injury. This is particularly useful for severe sprains or strains where the risk of additional damage is high.
Professional Treatment Options for Strains and Sprains
For more comprehensive management of sprains and strains, professional treatment options can play a crucial role in enhancing recovery and addressing any underlying issues. These treatments often complement initial self-care strategies and can help accelerate healing, restore function, and prevent future injuries.
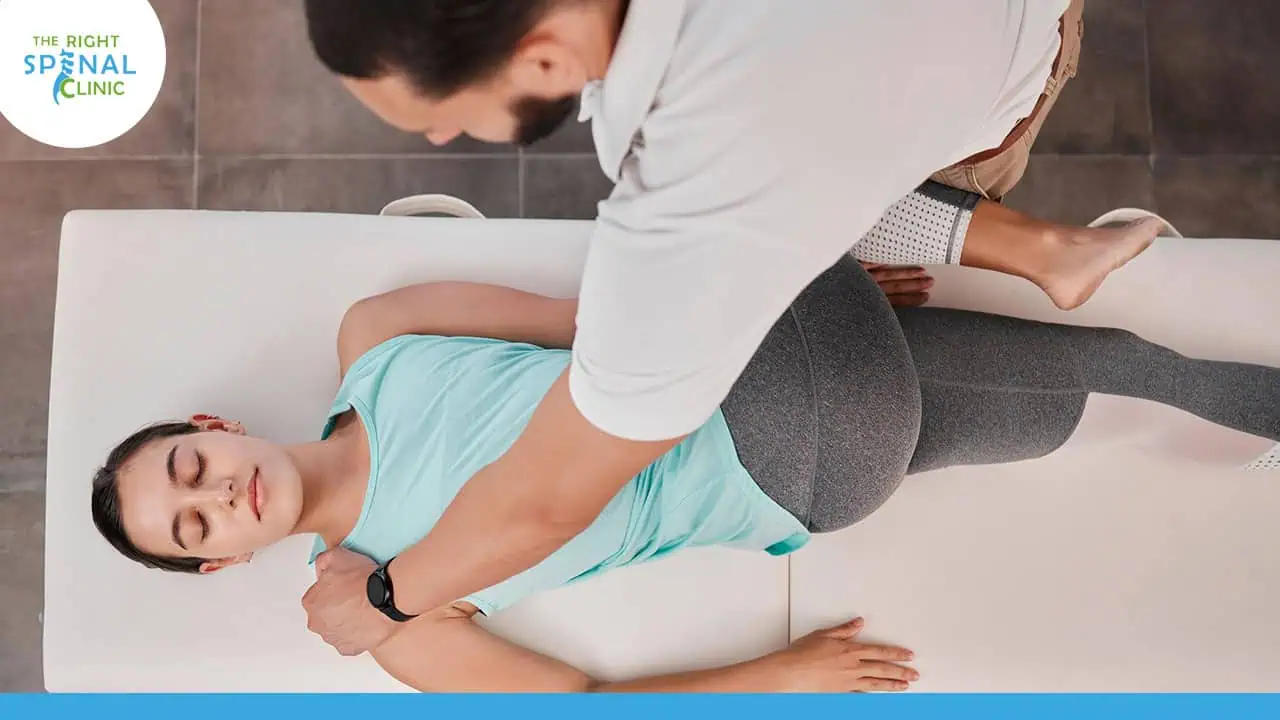
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a tailored rehabilitation program that includes:
- Strengthening Exercises: To rebuild muscle strength and support the injured area.
- Flexibility Exercises: To improve the range of motion and reduce stiffness.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to relieve pain, reduce swelling, and improve mobility.
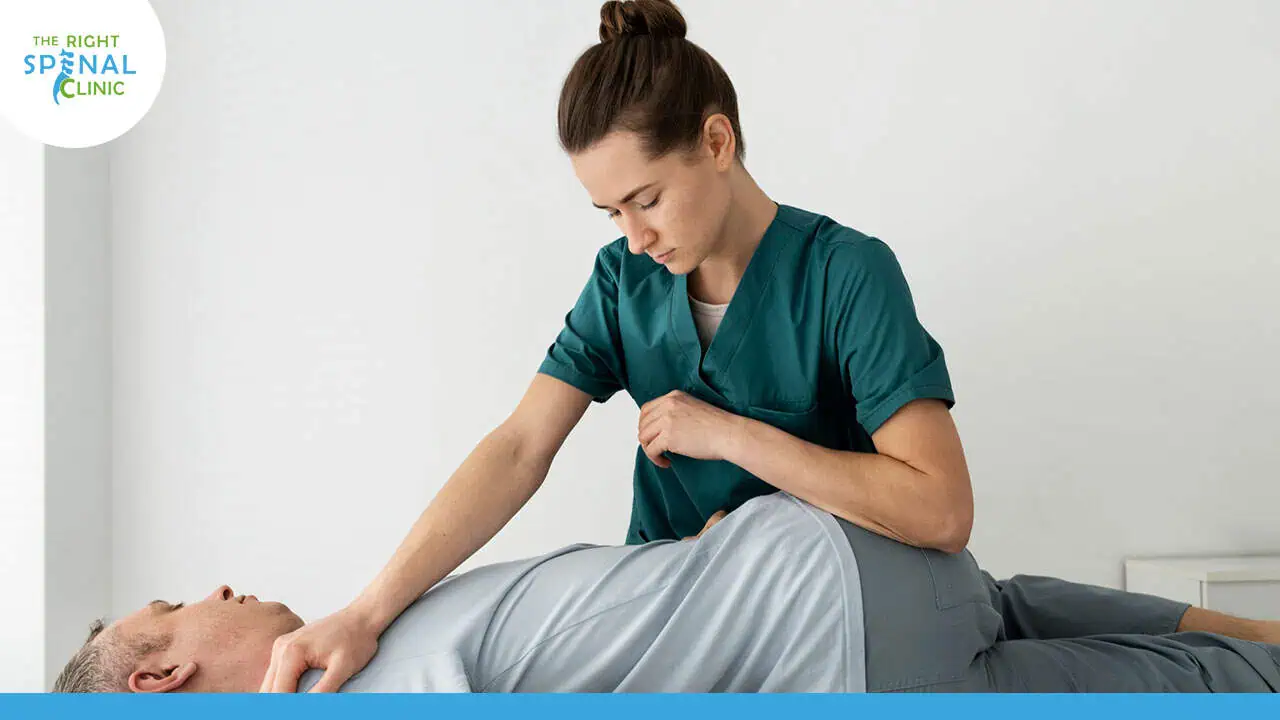
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors can provide:
- Spinal Alignment: Adjustments to ensure proper alignment of the spine, which can alleviate stress on the injured areas and improve overall function.
- Soft Tissue Therapy: Techniques to treat muscle tension and promote healing in the soft tissues surrounding the injury.
- Ultrasound Therapy: This treatment uses high-frequency sound waves to:
- Promote Tissue Healing: Deep heating effects help increase blood flow and accelerate the repair of soft tissues.
- Reduce Inflammation: By reducing swelling and pain, ultrasound therapy supports a faster recovery process.
- Electrical Stimulation: Also known as electrotherapy, this technique involves:
- Reducing Pain: Electrical impulses can interfere with pain signals sent to the brain, providing relief.
- Improving Muscle Function: Stimulates muscle contractions to maintain or improve strength and function.
- Accelerating Recovery: Enhances circulation and promotes the healing of tissues.
- Bracing and Support: Depending on the severity of the injury, braces, supports, or orthotic devices may be used to:
- Stabilize the Injured Area: Provides support and reduces the risk of further injury by limiting movement.
- Enhance Recovery: Maintains proper alignment and reduces strain on the injured tissues during the healing process.
These professional treatments, combined with initial self-care measures, offer a comprehensive approach to managing sprains and strains, ensuring a more effective and speedy recovery.
The Right Spinal Clinic’s Approach
At The Right Spinal Clinic, we understand that every sprain and strain is unique, requiring a personalized approach to treatment and recovery. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing customized care plans that address your specific needs and support your journey to optimal health.
Personalized Treatment Plans:
- Comprehensive Assessment: We start with a thorough evaluation to accurately diagnose the extent of your injury and understand its impact on your overall health.
- Tailored Therapy: Based on your assessment, we develop a personalized treatment plan that may include physical therapy, chiropractic care, ultrasound therapy, and other modalities to enhance healing and restore function.
- Ongoing Support: Our team is committed to guiding you through every stage of recovery, offering expert advice and adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
If you’re experiencing a sprain or strain and need expert care, don’t hesitate to reach out to The Right Spinal Clinic. Contact us today for a consultation, and let our skilled professionals help you get back to your best self.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between sprains and strains is crucial for effectively managing these common injuries. Sprains involve damage to ligaments around a joint, while strains affect muscles or tendons. Key symptoms include pain, swelling, and bruising, though their locations and causes may vary.
Proper treatment is essential to ensure a full recovery and prevent complications. Immediate self-care measures, such as the RICE method and over-the-counter pain relief, are important for managing symptoms initially. However, professional care from a healthcare provider can offer a comprehensive approach to healing, including physical therapy, chiropractic care, and specialized treatments like ultrasound and electrical stimulation.
If you experience severe symptoms, persistent pain, or significant functional limitations, seeking professional evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. At The Right Spinal Clinic, we provide personalized care plans to support your recovery and help you return to your normal activities.
Don’t wait to get the help you need—contact The Right Spinal Clinic today to schedule a consultation and start your path to recovery.
Recent Posts











